How to choose a process for product development
– Rapid Tooling & Injection Molding
To continue our last article, this paper presents the right process selection for low volume production of product development. When rapid prototyping is only suitable for small scale production (usually 1-20 pieces), but not often used for larger production and long-term operations, we have rapid tooling and rapid injection molding for you to move forward the product development into low volume and fast production before the former large production.
Along with the tighter and tighter developing cycle time request of new product, conventional mold making practice that depends on machining operations to generate the desired mold cavity is not competitive any longer. Therefore, quicker manufacturing process is developing incrementally in recent years.
Rapid tooling (Alternative name: proto mold, bridge tooling, quick-turn injection mold), is a simplified tooling making process that core and cavity inserts using rapid prototyping-based processes in just several steps starting from 3D data models, reducing tooling development time by 30-40% or more. With flexible design of mold and application of some manual inserts, the tooling cost will be about 30%-40% of conventioal tooling. It’s available for prototyping, low volume production, and on-demand injection molding.
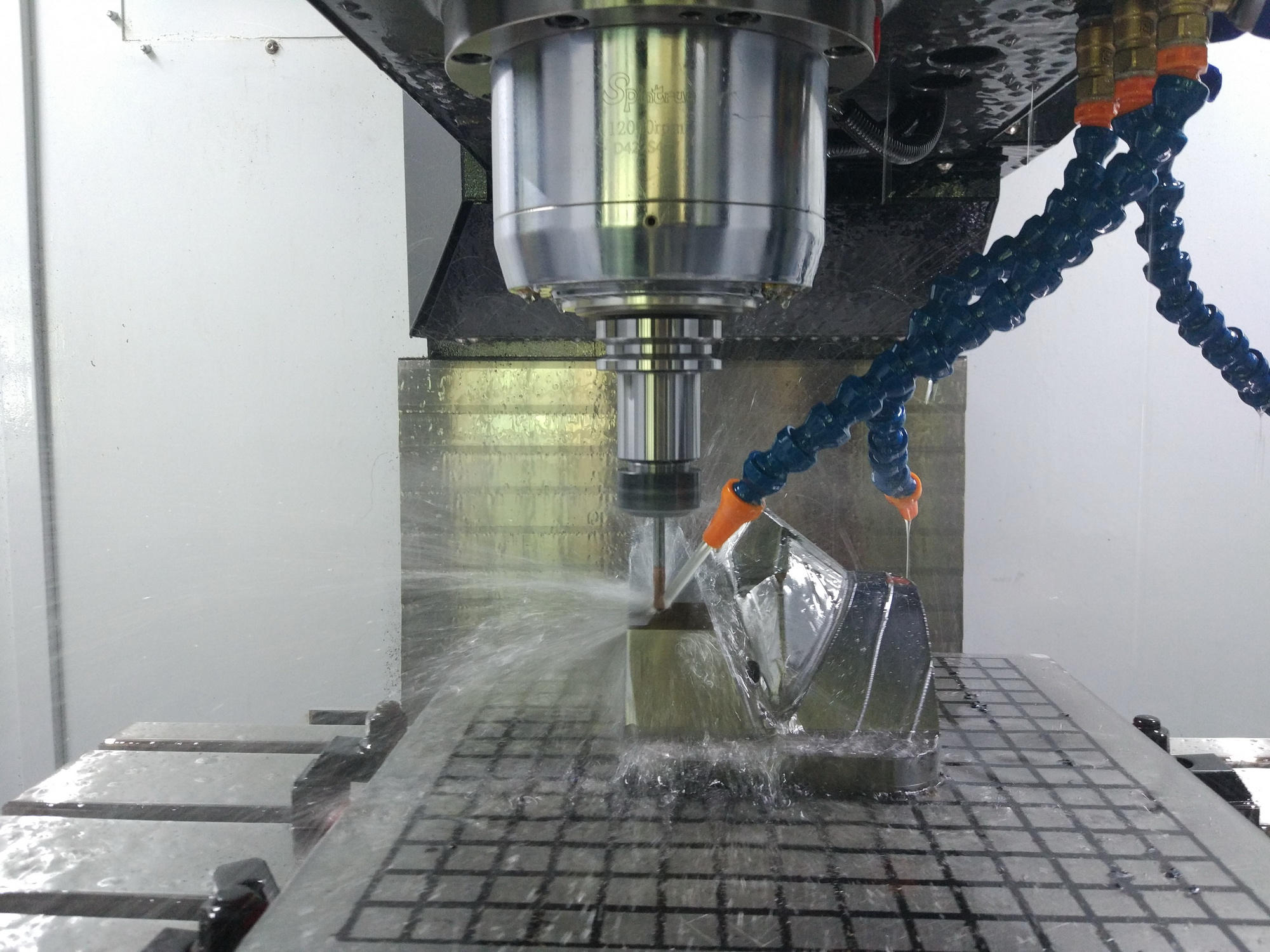

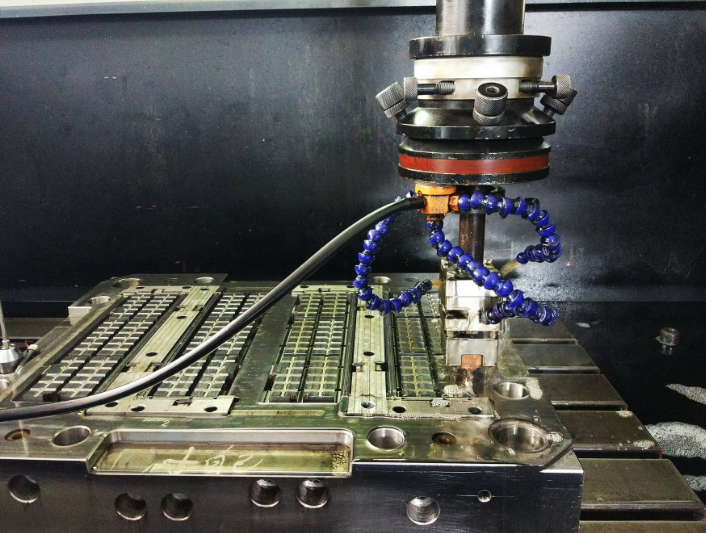
In many of rapid tooling factories, CNC machining is the most important method to produce the injecti on mold, as it provides fast lead time, relative accuracy, and good predictor of manufacturability during production, though it may require modifications to the design to allow CNC machining of certain features, such as radius and draft angles. Undercuts also require special consideration with this tooling approach. With CNC machining, tooling costs can make the process appear to be more expensive than others, but cost per finished piece is usually significantly lower than additive processes or CNC machining.
However, there’s still some limitation of CNC machining, especially when machining some special features like undercut, sharp corner, sharp V-shape, or narrow groove, etc., many of which can be overcome with conventional rapid tooling. Conventional mold building techniques can be applied to rapid tooling to allow more advanced geometry than allowed by CNC machined rapid tooling, while still delivering shorter lead times than production tooling.
EDM (electronic discharge machining) is the frequently-used conventional process to achieve the special features (mentioned above), it gives more possibility and less limitation to designer to design the parts, and the mod makers can design the molds flexibly with low cost. With EDM technology, more complex part structures and tight tolerance can be achieved, though it cost more and need longer time. Modifications are possible, but the cost is also higher than for other methods.
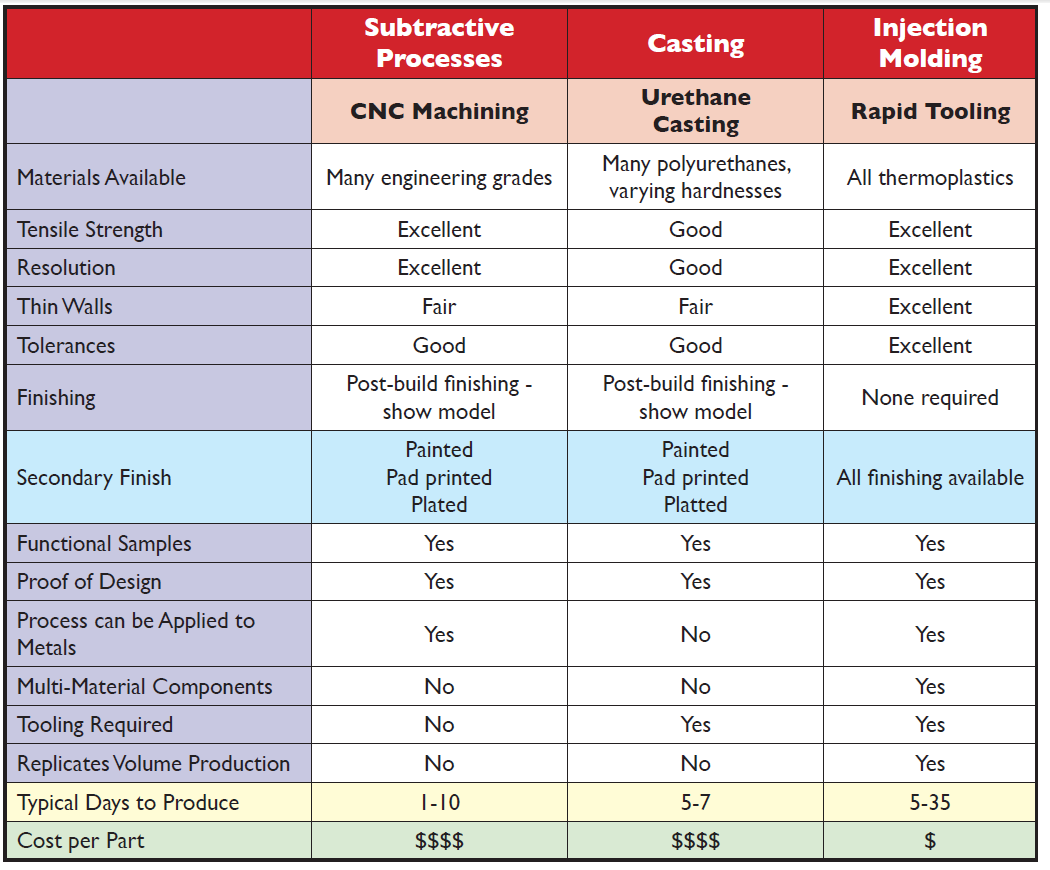
Here we would like to present the comparison of CNC machining, Polyurethane vacuum casting and rapid tooling.
Dank Mold will keep sharing much more tooling and injection molding knowledge at our website www.dankemold.com. If you were developing a new project, looking for mold maker, on-demand injection molding manufacturer, or a low-volume production company, email us via info@dankemold.com. We will response in 12 hours.
